Edge coloring
In graph theory, an edge coloring of a graph is an assignment of “colors” to the edges of the graph so that no two adjacent edges have the same color. For example, the figure to the right shows an edge coloring of a graph by the colors red, blue, and green. Edge colorings are one of several different types of graph coloring. The edge-coloring problem asks whether it is possible to color the edges of a given graph using at most k different colors, for a given value of k, or with the fewest possible colors. The minimum required number of colors for the edges of a given graph is called the chromatic index of the graph. For example, the edges of the graph in the illustration can be colored by three colors but cannot be colored by two colors, so the graph shown has chromatic index three.
By Vizing's theorem, the number of colors needed to edge color a simple graph is either its maximum degree Δ or Δ+1. For some graphs, such as bipartite graphs and high-degree planar graphs, the number of colors is always Δ, and for multigraphs, the number of colors may be as large as 3Δ/2. There are polynomial time algorithms that construct optimal colorings of bipartite graphs, and colorings of non-bipartite simple graphs that use at most Δ+1 colors; however, the general problem of finding an optimal edge coloring is NP-complete and the fastest known algorithms for it take exponential time. Many variations of the edge coloring problem, in which an assignments of colors to edges must satisfy other conditions than non-adjacency, have been studied. Edge colorings have applications in scheduling problems and in frequency assignment for fiber optic networks.
Contents |
Examples
A cycle graph may have its edges colored with two colors if the length of the cycle is even: simply alternate the two colors around the cycle. However, if the length is odd, three colors are needed.[1]
A complete graph Kn with n vertices may have its edges colored with n − 1 colors when n is an even number; this is a special case of Baranyai's theorem. Soifer (2008) provides the following geometric construction of a coloring in this case: place n points at the vertices and center of a regular (n − 1)-sided polygon. For each color class, include one edge from the center to one of the polygon vertices, and all of the perpendicular edges connecting pairs of polygon vertices. However, when n is odd, n colors are needed: each color can only be used for (n − 1)/2 edges, a 1/n fraction of the total.[2]
Several authors have studied edge colorings of the odd graphs, n-regular graphs in which the vertices represent teams of n − 1 players selected from a pool of 2n - 1 players, and in which the edges represent possible pairings of these teams (with one player left as "odd man out" to referee the game). The case that n = 3 gives the well-known Petersen graph. As Biggs (1972) explains the problem (for n = 6), the players wish to find a schedule for these pairings such that each team plays each of its six games on different days of the week, with Sundays off for all teams; that is, formalizing the problem mathematically, they wish to find a 6-edge-coloring of the 6-regular odd graph O6. When n is 3, 4, or 8, an edge coloring of On requires n + 1 colors, but when it is 5, 6, or 7, only n colors are needed.[3]
Definitions
As with its vertex counterpart, an edge coloring of a graph, when mentioned without any qualification, is always assumed to be a proper coloring of the edges, meaning no two adjacent edges are assigned the same color. Here, two edges are considered to be adjacent when they share a common vertex. An edge coloring of a graph G may also be thought of as equivalent to a vertex coloring of the line graph L(G), the graph that has a vertex for every edge of G and an edge for every pair of adjacent edges in G.
A proper edge coloring with k different colors is called a (proper) k-edge-coloring. A graph that can be assigned a (proper) k-edge-coloring is said to be k-edge-colorable. The smallest number of colors needed in a (proper) edge coloring of a graph G is the chromatic index, or edge chromatic number, χ′(G). The chromatic index is also sometimes written using the notation χ1(G); in this notation, the subscript one indicates that edges are one-dimensional objects. A graph is k-edge-chromatic if its chromatic index is exactly k. The chromatic index should not be confused with the chromatic number χ(G) or χ0(G), the minimum number of colors needed in a proper vertex coloring of G.
Unless stated otherwise all graphs are assumed to be simple, in contrast to multigraphs in which two or more edges may connecting the same pair of endpoints and in which there may be self-loops. For many problems in edge coloring, simple graphs behave differently from multigraphs, and additional care is needed to extend theorems about edge colorings of simple graphs to the multigraph case.
Relation to matching
A matching in a graph G is a set of edges, no two of which are adjacent; a perfect matching is a matching that includes edges touching all of the vertices of the graph, and a maximum matching is a matching that includes as many edges as possible. In an edge coloring, the set of edges with any one color must all be non-adjacent to each other, so they form a matching. That is, a proper edge coloring is the same thing as a partition of the graph into disjoint matchings.
If the size of a maximum matching in a given graph is small, then many matchings will be needed in order to cover all of the edges of the graph. Expressed more formally, this reasoning implies that if a graph has m edges in total, and if at most β edges may belong to a maximum matching, then every edge coloring of the graph must use at least m/β different colors.[4] For instance, the 16-vertex planar graph shown in the illustration has m = 24 edges. In this graph, there can be no perfect matching; for, if the center vertex is matched, the remaining unmatched vertices may be grouped into three different connected components with four, five, and five vertices, and the components with an odd number of vertices cannot be perfectly matched. However, the graph has maximum matchings with seven edges, so β = 7. Therefore, the number of colors needed to edge-color the graph is at least 24/7, and since the number of colors must be an integer it is at least four.
For a regular graph of degree k that does not have a perfect matching, this lower bound can be used to show that at least k + 1 colors are needed.[4] In particular, this is true for a regular graph with an odd number of vertices (such as the odd complete graphs); for such graphs, by the handshaking lemma, k must itself be even. However, the inequality χ′ ≥ m/β does not fully explain the chromatic index of every regular graph, because there are regular graphs that do have perfect matchings but that are not k-edge-colorable. For instance, the Petersen graph is regular, with m = 15 and with β = 5 edges in its perfect matchings, but it does not have a 3-edge-coloring.
Relation to degree
Vizing's theorem
The edge chromatic number of a graph G is very closely related to the maximum degree Δ(G), the largest number of edges incident to any single vertex of G. Clearly, χ′(G) ≥ Δ(G), for if Δ different edges all meet at the same vertex v, then all of these edges need to be assigned different colors from each other, and that can only be possible if there are at least Δ colors available to be assigned. Vizing's theorem (named for Vadim G. Vizing who published it in 1964) states that this bound is almost tight: for any graph, the edge chromatic number is either Δ(G) or Δ(G) + 1. When χ′(G) = Δ(G), G is said to be of class 1; otherwise, it is said to be of class 2.
For instance, when Δ(G) = 1, the graph G must itself be a matching, with no two edges adjacent, and its edge chromatic number is one. That is, all graphs with Δ(G) = 1 are of class 1. When Δ(G) = 2, the graph G must be a disjoint union of paths and cycles; in this case, it can be 2-edge-colored if and only if all of the cycles have even length. That is, a graph with Δ(G) = 2 is of class 1 if and only if it is bipartite. More generally, according to a theorem of Kőnig (1916), every bipartite graph is of class 1, regardless of its maximum degree. However, for non-bipartite graphs with larger maximum degree than two, it is much more difficult to distinguish class 1 graphs from class 2 graphs: Holyer (1981) proved that it is NP-complete to determine whether a graph is of class 1.
Several authors have provided additional conditions that classify some graphs as being of class 1 or class 2, but do not provide a complete classification. For instance, if the vertices of the maximum degree Δ in a graph G form an independent set, or more generally if the induced subgraph for this set of vertices is a forest, then G must be of class 1.[5]
Erdős & Wilson (1977) showed that almost all graphs are of class 1. That is, in the Erdős–Rényi model of random graphs, in which all n-vertex graphs are equally likely, let p(n) be the probability that an n-vertex graph drawn from this distribution is of class 1; then p(n) approaches one in the limit as n goes to infinity. For more precise bounds on the rate at which p(n) converges to one, see Frieze et al. (1988).
Regular graphs
A 1-factorization of a k-regular graph, a partition of the edges of the graph into perfect matchings, is the same thing as a k-edge-coloring of the graph. That is, a regular graph has a 1-factorization if and only if it is of class 1. As a special case of this, a 3-edge-coloring of a cubic (3-regular) graph is sometimes called a Tait coloring.
Not every regular graph has a 1-factorization; for instance, the Petersen graph does not. More generally the snarks are defined as the graphs that, like the Petersen graph, are bridgeless, 3-regular, and of class 2.
According to the theorem of Kőnig (1916), every bipartite regular graph has a 1-factorization. The theorem was stated earlier in terms of projective configurations and was proven by Ernst Steinitz in his PhD thesis.
Planar graphs
Vizing (1965) showed that a planar graph is of class 1 if its maximum degree is at least eight. In contrast, he observed that for any maximum degree in the range from two to five, there exist planar graphs of class 2. For degree two, any odd cycle is such a graph, and for degree three, four, and five, these graphs can be constructed from platonic solids by replacing a single edge by a path of two adjacent edges.
In Vizing's planar graph conjecture, Vizing (1965) states that all simple, planar graphs with maximum degree six or seven are of class 1, closing the remaining possible cases. Sanders & Zhao (2001) partially proved Vizing's planar graph conjecture by showing that all planar graphs with maximum degree seven are of class 1. Thus, the only case of the conjecture that remains unsolved is that of maximum degree six. This conjecture has implications for the total coloring conjecture.
The planar graphs of class 2 constructed by subdivision of the platonic solids are not regular: they have vertices of degree two as well as vertices of higher degree. The four color theorem, on vertex coloring of planar graphs, is equivalent to the statement that every bridgeless 3-regular planar graph is of class one (Tait 1880). This statement is now known to be true, due to the proof of the four color theorem by Appel & Haken (1976).
Graphs on nonplanar surfaces
In 1969, Branko Grünbaum conjectured that every 3-regular graph with a polyhedral embedding on any two-dimensional oriented manifold such as a torus must be of class one. In this context, a polyhedral embedding is a graph embedding such that every face of the embedding is topologically a disk and such that the dual graph of the embedding is simple, with no self-loops or multiple adjacencies. If true, this would be a generalization of the four color theorem, which was shown by Tait to be equivalent to the statement that 3-regular graphs with a polyhedral embedding on a sphere are of class one. However, Kochol (2009) showed the conjecture to be false by finding snarks that have polyhedral embeddings on high-genus orientable surfaces. Based on this construction, he also showed that it is NP-complete to tell whether a polyhedrally embedded graph is of class 1.[6]
Multigraphs
For multigraphs, in which multiple parallel edges may connect the same two vertices, results that are similar to but weaker than Vizing's theorem are known relating the edge chromatic number χ′(G), the maximum degree Δ(G), and the multiplicity μ(G), the maximum number of edges in any bundle of parallel edges. As a simple example showing that Vizing's theorem does not generalize to multigraphs, consider a Shannon multigraph, a multigraph with three vertices and three bundles of μ(G) parallel edges connecting each of the three pairs of vertices. In this example, Δ(G) = 2μ(G) (each vertex is incident to only two out of the three bundles of μ(G) parallel edges) but the edge chromatic number is 3μ(G) (there are 3μ(G) edges in total, and every two edges are adjacent, so all edges must be assigned different colors to each other). In a result that inspired Vizing,[7] Shannon (1949) showed that this is the worst case: χ′(G) ≤ (3/2)Δ(G) for any multigraph G. Additionally, for any multigraph G, χ′(G) ≤ Δ(G) + μ(G), an inequality that reduces to Vizing's theorem in the case of simple graphs (for which μ(G) = 1).
Algorithms
Because the problem of testing whether a graph is class 1 is NP-complete, there is no known polynomial time algorithm for edge-coloring every graph with an optimal number of colors. Nevertheless a number of algorithms have been developed that relax one or more of these criteria: they only work on a subset of graphs, or they do not always use an optimal number of colors, or they do not always run in polynomial time.
Optimally coloring special classes of graphs
In the case of bipartite graphs or multigraphs with maximum degree Δ, the optimal number of colors is exactly Δ. Cole, Ost & Schirra (2001) showed that an optimal edge coloring of these graphs can be found in the near-linear time bound O(m log Δ), where m is the number of edges in the graph; simpler, but somewhat slower, algorithms are described by Cole & Hopcroft (2002) and Alon (2003). The algorithm of Alon (2003) begins by making the input graph regular, without increasing its degree or significantly increasing its size, by merging pairs of vertices that belong to the same side of the bipartition and then adding a small number of additional vertices and edges. Then, if the degree is odd, Alon finds a single perfect matching in near-linear time, assigns it a color, and removes it from the graph, causing the degree to become even. Finally, Alon applies an observation of Gabow (1976), that selecting alternating subsets of edges in an Euler tour of the graph partitions it into two regular subgraphs, to split the edge coloring problem into two smaller subproblems, and his algorithm solves the two subproblems recursively. The total time for his algorithm is O(m log m).
For planar graphs with maximum degree Δ ≥ 7, the optimal number of colors is again exactly Δ. With the stronger assumption that Δ ≥ 9, it is possible to find an optimal edge coloring in linear time (Cole & Kowalik 2008).
Algorithms that use more than the optimal number of colors
Misra & Gries (1992) describe a polynomial time algorithm for coloring any graph with Δ + 1 colors, where Δ is the maximum degree of the graph. That is, the algorithm uses the optimal number of colors for graphs of class 2, and uses at most one more color than necessary for all graphs. Their algorithm follows the same strategy as Vizing's original proof of his theorem: it starts with an uncolored graph, and then repeatedly finds a way of recoloring the graph in order to increase the number of colored edges by one. More specifically, suppose that uv is an uncolored edge in a partially colored graph. The algorithm of Misra and Gries may be interpreted as constructing a directed pseudoforest P (a graph in which each vertex has at most one outgoing edge) on the neighbors of u: for each neighbor p of u, the algorithm finds a color c that is not used by any of the edges incident to p, finds the vertex q (if it exists) for which edge uq has color c, and adds pq as an edge to P. If the pseudoforest P constructed in this way contains a path from v to a vertex w that has no outgoing edges in P, then there is a color c that is available both at u and w. Recoloring edge uw with color c allows the remaining edge colors to be shifted one step along this path: for each vertex p in the path, edge up takes the color that was previously used by the successor of p in the path. This leads to a new coloring that includes edge uv. If, on the other hand, the path starting from v in the pseudoforest P leads to a cycle, let w be the neighbor of u at which the path joins the cycle, let c be the color of edge uw, and let d be a color that is not used by any of the edges at vertex u. Then swapping colors c and d on a Kempe chain either breaks the cycle or the edge on which the path joins the cycle, leading to the previous case. With some simple data structures to keep track of the colors that are used and available at each vertex, the construction of P and the recoloring steps of the algorithm can all be implemented in time O(n), where n is the number of vertices in the input graph. Since these steps need to be repeated m times, with each repetition increasing the number of colored edges by one, the total time is O(mn). In an unpublished technical report, Gabow et al. (1985) claimed a faster 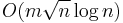 time bound for the same problem of coloring with Δ + 1 colors.
time bound for the same problem of coloring with Δ + 1 colors.
For multigraphs, Karloff & Shmoys (1987) present the following algorithm, which they attribute to Eli Upfal. Make the input multigraph G Eulerian by adding a new vertex connected by an edge to every odd-degree vertex, find an Euler tour, and choose an orientation for the tour. Form a bipartite graph H in which there are two copies of each vertex of G, one on each side of the bipartition, with an edge from a vertex u on the left side of the bipartition to a vertex v on the right side of the bipartition whenever the oriented tour has an edge from u to v in G. Apply a bipartite graph edge coloring algorithm to H. Each color class in H corresponds to a set of edges in G that form a subgraph with maximum degree two; that is, a disjoint union of paths and cycles, so for each color class in H it is possible to form three color classes in G. The time for the algorithm is bounded by the time to edge color a bipartite graph, O(m log Δ) using the algorithm of Cole, Ost & Schirra (2001). The number of colors this algorithm uses is at most 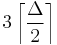 , close to but not quite the same as Shannon's bound of
, close to but not quite the same as Shannon's bound of 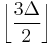 . It may also be made into a parallel algorithm in a straightforward way. In the same paper, Karloff and Shmoys also present a linear time algorithm for coloring multigraphs of maximum degree three with four colors (matching both Shannon's and Vizing's bounds) that operates on similar principles: their algorithm adds a new vertex to make the graph Eulerian, finds an Euler tour, and then chooses alternating sets of edges on the tour to split the graph into two subgraphs of maximum degree two. The paths and even cycles of each subgraph may be colored with two colors per subgraph. After this step, each remaining odd cycle contains at least one edge that may be colored with one of the two colors belonging to the opposite subgraph. Removing this edge from the odd cycle leaves a path, which may be colored using the two colors for its subgraph.
. It may also be made into a parallel algorithm in a straightforward way. In the same paper, Karloff and Shmoys also present a linear time algorithm for coloring multigraphs of maximum degree three with four colors (matching both Shannon's and Vizing's bounds) that operates on similar principles: their algorithm adds a new vertex to make the graph Eulerian, finds an Euler tour, and then chooses alternating sets of edges on the tour to split the graph into two subgraphs of maximum degree two. The paths and even cycles of each subgraph may be colored with two colors per subgraph. After this step, each remaining odd cycle contains at least one edge that may be colored with one of the two colors belonging to the opposite subgraph. Removing this edge from the odd cycle leaves a path, which may be colored using the two colors for its subgraph.
A greedy coloring algorithm that considers the edges of a graph or multigraph one by one, assigning each edge the first available color, may sometimes use as many as 2Δ − 1 colors, which may be nearly twice as many number of colors as is necessary. However, it has the advantage that it may be used in the online algorithm setting in which the input graph is not known in advance; in this setting, its competitive ratio is two, and this is optimal: no other online algorithm can achieve a better performance.[8] However, if edges arrive in a random order, and the input graph has a degree that is at least logarithmic, then smaller competitive ratios can be achieved.[9]
Several authors have made conjectures that imply that the fractional chromatic index of any multigraph (a number that can be computed in polynomial time using linear programming) is within one of the chromatic index.[10] If these conjectures are true, it would be possible to compute a number that is never more than one off from the chromatic index in the multigraph case, matching what is known via Vizing's theorem for simple graphs. Although unproven in general, these conjectures are known to hold when the chromatic index is at least 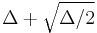 , as can happen for multigraphs with sufficiently large multiplicity.[11]
, as can happen for multigraphs with sufficiently large multiplicity.[11]
Exact algorithms
It is straightforward to test whether a graph may be edge colored with one or two colors, so the first nontrivial case of edge coloring is testing whether a graph has a 3-edge-coloring. As Kowalik (2009) showed, it is possible to test whether a graph has a 3-edge-coloring in time O(1.344n), while using only polynomial space. Although this time bound is exponential, it is significantly faster than a brute force search over all possible assignments of colors to edges. Every biconnected 3-regular graph with n vertices has O(2n/2) 3-edge-colorings; all of which can be listed in time O(2n/2) (somewhat slower than the time to find a single coloring); as Greg Kuperberg observed, the graph of a prism over an n/2-sided polygon has many colorings, showing that this bound is tight.[12]
By applying exact algorithms for vertex coloring to the line graph of the input graph, it is possible to optimally edge-color any graph with m edges, regardless of the number of colors needed, in time 2mmO(1) and exponential space, or in time O(2.2461m) and only polynomial space (Björklund, Husfeldt & Koivisto 2009).
Because edge coloring is NP-complete even for three colors, it is unlikely to be fixed parameter tractable when parametrized by the number of colors. However, it is tractable for other parameters. In particular, Zhou, Nakano & Nishizeki (1996) showed that for graphs of treewidth w, an optimal edge coloring can be computed in time O(nw(6w)w(w + 1)/2), a bound that depends superexponentially on w but only linearly on the number n of vertices in the graph.
Nemhauser & Park (1991) formulate the edge coloring problem as an integer program and describe their experience using an integer programming solver to edge color graphs. However, they did not perform any complexity analysis of their algorithm.
Additional properties
A graph is uniquely k-edge-colorable if there is only one way of partitioning the edges into k color classes, ignoring the k! possible permutations of the colors. For k ≠ 3, the only uniquely k-edge-colorable graphs are paths, cycles, and stars, but for k = 3 other graphs may also be uniquely k-edge-colorable. Every uniquely 3-edge-colorable graph has exactly three Hamiltonian cycles (formed by deleting one of the three color classes) but there exist 3-regular graphs that have three Hamiltonian cycles and are not uniquely 3-colorable, such as the generalized Petersen graphs G(6n + 3, 2) for n ≥ 2. The only known nonplanar uniquely 3-colorable graph is the generalized Petersen graph G(9,2), and it has been conjectured that no others exist.[13]
Folkman & Fulkerson (1969) investigated the non-increasing sequences of numbers m1, m2, m3, ... with the property that there exists a proper edge coloring of a given graph G with m1 edges of the first color, m2 edges of the first color, etc. They observed that, if a sequence P is feasible in this sense, and is greater in lexicographic order than a sequence Q with the same sum, then Q is also feasible. For, if P > Q in lexicographic order, then P can be transformed into Q by a sequence of steps, each of which reduces one of the numbers mi by one unit and increases another later number mj with i < j by one unit. In terms of edge colorings, starting from a coloring that realizes P, each of these same steps may be performed by swapping colors i and j on a Kempe chain, a maximal path of edges that alternate between the two colors. In particular, any graph has an equitable edge coloring, an edge coloring with an optimal number of colors in which every two color classes differ in size by at most one unit.
The De Bruijn–Erdős theorem may be used to transfer many edge coloring properties of finite graphs to infinite graphs. For instance, Shannon's and Vizing's theorems relating the degree of a graph to its chromatic index both generalize straightforwardly to infinite graphs.[14]
Richter (2011) considers the problem of finding a graph drawing of a given cubic graph with the properties that all of the edges in the drawing have one of three different slopes and that no two edges lie on the same line as each other. If such a drawing exists, then clearly the slopes of the edges may be used as colors in a 3-edge-coloring of the graph. For instance, the drawing of the utility graph K3,3 as the edges and long diagonals of a regular hexagon represents a 3-edge-coloring of the graph in this way. As Richter shows, a 3-regular simple bipartite graph, with a given Tait coloring, has a drawing of this type that represents the given coloring if and only if the graph is 3-edge-connected. For a non-bipartite graph, the condition is a little more complicated: a given coloring can be represented by a drawing if the bipartite double cover of the graph is 3-edge-connected, and if deleting any monochromatic pair of edges leads to a subgraph that is still non-bipartite. These conditions may all be tested easily in polynomial time; however, the problem of testing whether a 4-edge-colored 4-regular graph has a drawing with edges of four slopes, representing the colors by slopes, is complete for the existential theory of the reals, a complexity class at least as difficult as being NP-complete.
As well as being related to the maximum degree and maximum matching number of a graph, the chromatic index is closely related to the linear arboricity la(G) of a graph G, the minimum number of linear forests (disjoint unions of paths) into which the graph's edges may be partitioned. A matching is a special kind of linear forest, and in the other direction, any linear forest can be 2-edge-colored, so for every G it follows that la(G) ≤ χ′(G) ≤ 2 la(G). Akiyama's conjecture states that 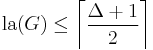 , from which it would follow more strongly that 2 la(G) − 2 ≤ χ′(G) ≤ 2 la(G). For graphs of maximum degree three, la(G) is always exactly two, so in this case the bound χ′(G) ≤ 2 la(G) matches the bound given by Vizing's theorem.[15]
, from which it would follow more strongly that 2 la(G) − 2 ≤ χ′(G) ≤ 2 la(G). For graphs of maximum degree three, la(G) is always exactly two, so in this case the bound χ′(G) ≤ 2 la(G) matches the bound given by Vizing's theorem.[15]
Other types of edge coloring
The Thue number of a graph is the number of colors required in an edge coloring meeting the stronger requirement that, in every even-length path, the first and second halves of the path form different sequences of colors.
The arboricity of a graph is the minimum number of colors required so that the edges of each color have no cycles (rather than, in the standard edge coloring problem, having no adjacent pairs of edges). That is, it is the minimum number of forests into which the edges of the graph may be partitioned into.[16] Unlike the chromatic index, the arboricity of a graph may be computed in polynomial time.[17]
List edge-coloring is a problem in which one is given a graph in which each edge is associated with a list of colors, and must find a proper edge coloring in which the color of each edge is drawn from that edge's list. The list chromatic index of a graph G is the smallest number k with the property that, no matter how one chooses lists of colors for the edges, as long as each edge has at least k colors in its list, then a coloring is guaranteed to be possible. Thus, the list chromatic index is always at least as large as the chromatic index. The Dinitz conjecture on the completion of partial Latin squares may be rephrased as the statement that the list edge chromatic number of the complete bipartite graph Kn,n equals its edge chromatic number, n. Galvin (1995) resolved the conjecture by proving, more generally, that in every bipartite graph the chromatic index and list chromatic index are equal. The equality between the chromatic index and the list chromatic index has been conjectured to hold, even more generally, for arbitrary multigraphs with no self-loops; this conjecture remains open.
Many other commonly studied variations of vertex coloring have also been extended to edge colorings. For instance, complete edge coloring is the edge-coloring variant of complete coloring, a proper edge coloring in which each pair of colors must be represented by at least one pair of adjacent edges and in which the goal is to maximize the total number of colors.[18] Strong edge coloring is the edge-coloring variant of strong coloring, an edge coloring in which every two edges with adjacent endpoints must have different colors.[19] Strong edge coloring has applications in channel allocation schemes for wireless networks.[20] Acyclic edge coloring is the edge-coloring variant of acyclic coloring, an edge coloring for which every two color classes form an acyclic subgraph (that is, a forest).[21]
Eppstein (2008) studied 3-edge-colorings of cubic graphs with the additional property that no two bichromatic cycles share more than a single edge with each other. He showed that the existence of such a coloring is equivalent to the existence of a drawing of the graph on a three-dimensional integer grid, with edges parallel to the coordinate axes and each axis-parallel line containing at most two vertices. However, like the standard 3-edge-coloring problem, finding a coloring of this type is NP-complete.
Total coloring is a form of coloring that combines vertex and edge coloring, by requiring both the vertices and edges to be colored. Any incident pair of a vertex and an edge, or an edge and an edge, must have distinct colors, as must any two adjacent vertices. It has been conjectured (combining Vizing's theorem and Brooks' theorem) that any graph has a total coloring in which the number of colors is at most the maximum degree plus two, but this remains unproven.
If a 3-regular graph on a surface is 3-edge-colored, its dual graph forms a triangulation of the surface which is also edge colored (although not, in general, properly edge colored) in such a way that every triangle has one edge of each color. Other colorings and orientations of triangulations, with other local constraints on how the colors are arranged at the vertices or faces of the triangulation, may be used to encode several types of geometric object. For instance, rectangular subdivisions (partitions of a rectangular subdivision into smaller rectangles, with three rectangles meeting at every vertex) may be described combinatorially by a "regular labeling", a two-coloring of the edges of a triangulation dual to the subdivision, with the constraint that the edges incident to each vertex form four contiguous subsequences, within each of which the colors are the same. This labeling is dual to a coloring of the rectangular subdivision itself in which the vertical edges have one color and the horizontal edges have the other color. Similar local constraints on the order in which colored edges may appear around a vertex may also be used to encode straight-line grid embeddings of planar graphs and three-dimensional polyhedra with axis-parallel sides. For each of these three types of regular labelings, the set of regular labelings of a fixed graph forms a distributive lattice that may be used to quickly list all geometric structures based on the same graph (such as all axis-parallel polyhedra having the same skeleton) or to find structures satisfying additional constraints.[22]
A deterministic finite automaton may be interpreted as a directed graph in which each vertex has the same out-degree d, and in which the edges are d-colored in such a way that every two edges with the same source vertex have distinct colors. The road coloring problem is the problem of edge-coloring a directed graph with uniform out-degrees, in such a way that the resulting automaton has a synchronizing word. Trahtman (2009) solved the road coloring problem by proving that such a coloring can be found whenever the given graph is strongly connected and aperiodic.
Ramsey's theorem concerns the problem of k-coloring the edges of a large complete graph Kn in order to avoid creating monochromatic complete subgraphs Ks of some given size s. According to the theorem, there exists a number Rk(s) such that, whenever n ≥ R(s), such a coloring is not possible. For instance, R2(3) = 6, that is, if the edges of the graph K6 are 2-colored, there will always be a monochromatic triangle.
Applications
Edge colorings of complete graphs may be used to schedule a round-robin tournament into as few rounds as possible so that each pair of competitors plays each other in one of the rounds; in this application, the vertices of the graph correspond to the competitors in the tournament, the edges correspond to games, and the edge colors correspond to the rounds in which the games are played.[23] Similar coloring techniques may also be used to schedule other sports pairings that are not all-play-all; for instance, in the National Football League, the pairs of teams that will play each other in a given year are determined, based on the teams' records from the previous year, and then an edge coloring algorithm is applied to the graph formed by the set of pairings in order to assign games to the weekends on which they are played.[24] For this application, Vizing's theorem implies that no matter what set of pairings is chosen (as long as no teams play each other twice in the same season), it is always possible to find a schedule that uses at most one more weekend than there are games per team.
Open shop scheduling is a problem of scheduling production processes, in which there are a set of objects to be manufactured, each object has a set of tasks to be performed on it (in any order), and each task must be performed on a specific machine, preventing any other task that requires the same machine from being performed at the same time. If all tasks have the same length, then this problem may be formalized as one of edge coloring a bipartite multigraph, in which the vertices on one side of the bipartition represent the objects to be manufactured, the vertices on the other side of the bipartition represent the manufacturing machines, the edges represent tasks that must be performed, and the colors represent time steps in which each task may be performed. Since bipartite edge coloring may be performed in polynomial time, the same is true for this restricted case of open shop scheduling.[25]
Gandham, Dawande & Prakash (2005) study the problem of link scheduling for time division multiple access network communications protocols on sensor networks as a variant of edge coloring. In this problem, one must choose time slots for the edges of a wireless communications network so that each node of the network can communicate with each neighboring node without interference. Using a strong edge coloring (and using two time slots for each edge color, one for each direction) would solve the problem but might use more time slots than necessary. Instead, they seek a coloring of the directed graph formed by doubling each undirected edge of the network, with the property that each directed edge uv has a different color from the edges that go out from v and from the neighbors of v. They propose a heuristic for this problem based on a distributed algorithm for (Δ + 1)-edge-coloring together with a postprocessing phase that reschedules edges that might interfere with each other.
In fiber-optic communication, the path coloring problem is the problem of assigning colors (frequencies of light) to pairs of nodes that wish to communicate with each other, and paths through a fiber-optic communications network for each pair, subject to the restriction that no two paths that share a segment of fiber use the same frequency as each other. Paths that pass through the same communication switch but not through any segment of fiber are allowed to use the same frequency. When the communications network is arranged as a star network, with a single central switch connected by separate fibers to each of the nodes, the path coloring problem may be modeled exactly as a problem of edge coloring a graph or multigraph, in which the communicating nodes form the graph vertices, pairs of nodes that wish to communicate form the graph edges, and the frequencies that may be used for each pair form the colors of the edge coloring problem. For communications networks with a more general tree topology, local path coloring solutions for the star networks defined by each switch in the network may be patched together to form a single global solution.[26]
Open problems
Jensen & Toft (1995) list 23 open problems concerning edge coloring. They include:
- The conjecture of Gol'dberg (1973) that the chromatic index and fractional index are within one of each other, which would allow the chromatic index to be approximated within one color in polynomial time.
- Several conjectures of Jakobsen and others on the structure of critical graphs for edge coloring, graphs of class 2 such that any subgraph either has smaller maximum degree or is of class 1. Jakobsen originally conjectured that all critical graphs have an odd number of vertices, but this was eventually disproved. Several other conjectures weakening this one, or bounding the numbers of vertices of critical graphs and critical multigraphs, remain open.
- Vizing's problem of classifying the maximum degrees that are possible for class 2 planar graphs.
- The overfull subgraph conjecture of A. J. W. Hilton, stating that graphs with degree at least n/3 are either of class 1 or contain a subgraph with the same degree Δ as the original graph, and with an odd number k of vertices, such that the number of edges in the subgraph is greater than Δ(k − 1)/2, and a similar conjecture by Herbert Grötzsch and Paul Seymour concerning planar graphs in place of high-degree graphs.
- A conjecture of Chetwynd and Hilton (possibly going back earlier to the work of Gabriel Andrew Dirac that regular graphs with an even number n of vertices and with degree at least n/2 are of class 1.
- A conjecture of Claude Berge and D. R. Fulkerson that the 6-regular multigraphs formed by doubling every edge of a bridgeless 3
Notes
- ^ Soifer (2008), problem 16.4, p. 133.
- ^ Soifer (2008), problem 16.5, p. 133. The fact that either n or (n − 1) colors are needed is an instance of Vizing's theorem.
- ^ Biggs (1972); Meredith & Lloyd (1973); Biggs (1979).
- ^ a b Soifer (2008), p. 134.
- ^ Fournier (1973).
- ^ Kochol (2010).
- ^ Soifer (2008), p. 136.
- ^ Bar-Noy, Motwani & Naor (1992).
- ^ Bahmani, Mehta & Motwani (2010).
- ^ Gol'dberg (1973); Andersen (1977); Seymour (1979).
- ^ Chen, Yu & Zang (2011).
- ^ Eppstein (2008).
- ^ Schwenk (1989).
- ^ Bosák (1972).
- ^ Akiyama, Exoo & Harary (1980); Habib & Péroche (1982); Horák & Niepel (1985).
- ^ Nash-Williams (1964).
- ^ Gabow & Westermann (1992).
- ^ Bosák & Nešetřil (1976).
- ^ Fouquet & Jolivet (1983); Mahdian (2002); Frieze, Krivelevich & Sudakov (2005); Cranston (2006).
- ^ Barrett et al. (2006).
- ^ Alon, Sudakov & Zaks (2002); Muthu, Narayanan & Subramanian (2007).
- ^ Eppstein (2010).
- ^ Burke, De Werra & Kingston (2004).
- ^ Skiena (2008).
- ^ Williamson et al. (1997).
- ^ Erlebach & Jansen (2001).
References
- Akiyama, Jin; Exoo, Geoffrey; Harary, Frank (1980), "Covering and packing in graphs. III. Cyclic and acyclic invariants", Mathematica Slovaca 30 (4): 405–417, MR595302.
- Alon, Noga (2003), "A simple algorithm for edge-coloring bipartite multigraphs", Information Processing Letters 85 (6): 301–302, doi:10.1016/S0020-0190(02)00446-5, MR1956451.
- Alon, Noga; Sudakov, Benny; Zaks, Ayal (2001), "Acyclic edge colorings of graphs", Journal of Graph Theory 37 (3): 157–167, doi:10.1002/jgt.1010, MR1837021.
- Andersen, Lars Døvling (1977), "On edge-colourings of graphs", Mathematica Scandinavica 40 (2): 161–175, MR0465922. As cited by Chen, Yu & Zang (2011).
- Appel, K.; Haken, W. (1976), "Every planar map is four colorable", Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society 82 (5): 711–712, doi:10.1090/S0002-9904-1976-14122-5, MR0424602.
- Bahmani, Bahman; Mehta, Aranyak; Motwani, Rajeev (2010), "A 1.43-competitive online graph edge coloring algorithm in the random order arrival model", Proceedings of the Twenty-First Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms (SODA '10), pp. 31–39, http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1873601.1873605.
- Bar-Noy, Amotz; Motwani, Rajeev; Naor, Joseph (1992), "The greedy algorithm is optimal for on-line edge coloring", Information Processing Letters 44 (5): 251–253, doi:10.1016/0020-0190(92)90209-E.
- Barrett, C.L.; Istrate, G.; Kumar, V.S.A.; Marathe, M.V.; Thite, S.; Thulasidasan, S. (2006), "Strong Edge Coloring for Channel Assignment in Wireless Radio Networks", Proc. Fourth Annual IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops 2006), pp. 106, doi:10.1109/PERCOMW.2006.129, ISBN 0-7695-2520-2.
- Biggs, Norman (1972), An edge-colouring problem, in Guy, Richard K., "Research Problems", American Mathematical Monthly 79 (9): 1018–1020, JSTOR 2318076.
- Biggs, Norman (1979), Some odd graph theory, "Second International Conference on Combinatorial Mathematics", Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 319: 71–81, doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb32775.x.
- Björklund, Andreas; Husfeldt, Thore; Koivisto, Mikko (2009), "Set partitioning via inclusion-exclusion", SIAM Journal on Computing 39 (2): 546–563, doi:10.1137/070683933, MR2529771.
- Bosák, Juraj (1972), "Chromatic index of finite and infinite graphs", Czechoslovak Mathematical Journal 22(97): 272–290, MR0309777.
- Bosák, Juraj; Nešetřil, Jaroslav (1976), "Complete and pseudocomplete colourings of a graph", Matematicky Časopis Slovenskej Akadémie Vied 26 (3): 171–184, MR0439672.
- Burke, E.; De Werra, D.; Kingston, J. (2004), "5.6.5 Sports Timetabling", in J. L., Gross; J., Yellen, Handbook of Graph Theory, CRC Press, p. 462, ISBN 9781584880905, http://books.google.com/books?id=mKkIGIea_BkC&pg=PA462.
- Chen, Guantao; Yu, Xingxing; Zang, Wenan (2011), "Approximating the chromatic index of multigraphs", Journal of Combinatorial Optimization 21 (2): 219–246, doi:10.1007/s10878-009-9232-y, MR2770056.
- Cole, Richard; Hopcroft, John (1982), "On edge coloring bipartite graphs", SIAM Journal on Computing 11 (3): 540–546, doi:10.1137/0211043, MR664720.
- Cole, Richard; Kowalik, Łukasz (2008), "New linear-time algorithms for edge-coloring planar graphs", Algorithmica 50 (3): 351–368, doi:10.1007/s00453-007-9044-3, MR2366985.
- Cole, Richard; Ost, Kirstin; Schirra, Stefan (2001), "Edge-coloring bipartite multigraphs in O(E log D) time", Combinatorica 21 (1): 5–12, doi:10.1007/s004930170002, MR1805711.
- Cranston, Daniel W. (2006), "Strong edge-coloring of graphs with maximum degree 4 using 22 colors", Discrete Mathematics 306 (21): 2772–2778, doi:10.1016/j.disc.2006.03.053, MR2264374.
- Eppstein, David (2008), "The topology of bendless three-dimensional orthogonal graph drawing", in Tollis, Ioannis G.; Patrignani, Marizio, Proc. 16th Int. Symp. Graph Drawing, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 5417, Heraklion, Crete: Springer-Verlag, pp. 78–89, arXiv:0709.4087.
- Eppstein, David (2010), "Regular labelings and geometric structures", Proc. 22nd Canadian Conference on Computational Geometry (CCCG 2010), University of Manitoba, arXiv:1007.0221, http://www.cs.umanitoba.ca/~cccg2010/electronicProceedings/invitedpaper2.pdf.
- Erdős, Paul; Wilson, Robin J. (1977), "Note on the chromatic index of almost all graphs", Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B 23 (2–3): 255–257, doi:10.1016/0095-8956(77)90039-9, http://www.renyi.hu/~p_erdos/1977-20.pdf.
- Erlebach, Thomas; Jansen, Klaus (2001), "The complexity of path coloring and call scheduling", Theoretical Computer Science 255 (1–2): 33–50, doi:10.1016/S0304-3975(99)00152-8, MR1819065.
- Fiorini, S.; Wilson, Robin James (1977), Edge-colourings of graphs, Research Notes in Mathematics, 16, London: Pitman, ISBN 0-273-01129-4, MR0543798.
- Folkman, Jon; Fulkerson, D. R. (1969), "Edge colorings in bipartite graphs", Combinatorial Mathematics and its Applications (Proc. Conf., Univ. North Carolina, Chapel Hill, N.C., 1967), Chapel Hill, N.C.: Univ. North Carolina Press, pp. 561–577, MR0262112.
- Fouquet, J.-L.; Jolivet, J.-L. (1983), "Strong edge-colorings of graphs and applications to multi-k-gons", Ars Combinatoria 16 (A): 141–150, MR737086.
- Fournier, Jean-Claude (1973), "Colorations des arêtes d'un graphe", Cahiers du Centre d'Études de Recherche Opérationnelle 15: 311–314, MR0349458.
- Frieze, Alan M.; Jackson, B.; McDiarmid, C. J. H.; Reed, B. (1988), "Edge-colouring random graphs", Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B 45 (2): 135–149, doi:10.1016/0095-8956(88)90065-2, MR961145.
- Frieze, Alan M.; Krivelevich, Michael; Sudakov, Benny (2005), "The strong chromatic index of random graphs", SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathematics 19 (3): 719–727 (electronic), doi:10.1137/S0895480104445757, MR2191290.
- Gabow, Harold N. (1976), "Using Euler partitions to edge color bipartite multigraphs", International Journal of Computer and Information Sciences 5 (4): 345–355, doi:10.1007/BF00998632, MR0422081.
- Gabow, Harold N.; Nishizeki, Takao; Kariv, Oded; Leven, Daniel; Terada, Osamu (1985), Algorithms for edge-coloring graphs, Tech. Report TRECIS-8501, Tohoku University.
- Gabow, Harold N.; Westermann, Herbert H. (1992), "Forests, frames, and games: algorithms for matroid sums and applications", Algorithmica 7 (5–6): 465–497, doi:10.1007/BF01758774, MR1154585.
- F. Galvin (1995), "The list chromatic index of a bipartite multigraph", Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B 63 (1): 153–158, doi:10.1006/jctb.1995.1011.
- Gandham, S.; Dawande, M.; Prakash, R. (2005), "Link scheduling in sensor networks: distributed edge coloring revisited", Proc. 24th INFOCOM, 4, pp. 2492–2501, doi:10.1109/INFCOM.2005.1498534, ISBN 0-7803-8968-9.
- Gol'dberg, M. K. (1973), "Multigraphs with a chromatic index that is nearly maximal", Diskret. Analiz (23): 3–7, 72, MR0354429. As cited by Chen, Yu & Zang (2011).
- Habib, M.; Péroche, B. (1982), "Some problems about linear arboricity", Discrete Mathematics 41 (2): 219–220, doi:10.1016/0012-365X(82)90209-6, MR676882.
- Holyer, Ian (1981), "The NP-completeness of edge-coloring", SIAM Journal on Computing 10 (4): 718–720, doi:10.1137/0210055.
- Horák, Peter; Niepel, Ĺudovít (1982), "A short proof of a linear arboricity theorem for cubic graphs", Acta Mathematica Universitatis Comenianae 40/41: 275–277, MR686983.
- Jensen, Tommy R.; Toft, Bjarne (1995), Graph Coloring Problems, New York: Wiley-Interscience, ISBN 0-471-02865-7.
- Kochol, Martin (2009), "Polyhedral embeddings of snarks in orientable surfaces", Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, 137, pp. 1613–1619.
- Karloff, Howard J.; Shmoys, David B. (1987), "Efficient parallel algorithms for edge coloring problems", Journal of Algorithms 8 (1): 39–52, doi:10.1016/0196-6774(87)90026-5, MR875324.
- Kochol, Martin (2010), "Complexity of 3-edge-coloring in the class of cubic graphs with a polyhedral embedding in an orientable surface", Discrete Applied Mathematics 158 (16): 1856–1860, doi:10.1016/j.dam.2010.06.019, MR2679785.
- Kőnig, D. (1916), "Über Graphen und ihre Anwendung auf Determinantentheorie und Mengenlehre", Mathematische Annalen 77 (4): 453–465, doi:10.1007/BF01456961.
- Kowalik, Łukasz (2009), "Improved edge-coloring with three colors", Theoretical Computer Science 410 (38–40): 3733–3742, doi:10.1016/j.tcs.2009.05.005, MR2553326.
- Mahdian, Mohammad (2002), "On the computational complexity of strong edge coloring", Discrete Applied Mathematics 118 (3): 239–248, doi:10.1016/S0166-218X(01)00237-2, MR1892971.
- Meredith, Guy H. J.; Lloyd, E. Keith (1973), "The footballers of Croam", Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B 15 (2): 161–166, doi:10.1016/0095-8956(73)90016-6.
- Misra, J.; Gries, David (1992), "A constructive proof of Vizing's Theorem", Information Processing Letters 41 (3): 131–133, doi:10.1016/0020-0190(92)90041-S.
- Muthu, Rahul; Narayanan, N.; Subramanian, C. R. (2007), "Improved bounds on acyclic edge colouring", Discrete Mathematics 307 (23): 3063–3069, doi:10.1016/j.disc.2007.03.006, MR2371078.
- Nash-Williams, C. St. J. A. (1964), "Decomposition of finite graphs into forests", Journal of the London Mathematical Society, Second Series 39: 12, MR0161333
- Nemhauser, George L.; Park, Sungsoo (1991), "A polyhedral approach to edge coloring", Operations Research Letters 10 (6): 315–322, doi:10.1016/0167-6377(91)90003-8, MR1128970.
- Richter, David A. (2011), "How to Draw a Tait-Colorable Graph", in Brandes, Ulrik; Cornelsen, Sabine, Proc. 18th International Symposium on Graph Drawing (GD 2010), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 6502, Springer-Verlag, pp. 353–364, doi:10.1007/978-3-642-18469-7_32, ISBN 978-3-642-18468-0.
- Sanders, Daniel P.; Zhao, Yue (2001), "Planar graphs of maximum degree seven are class I", Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B 83 (2): 201–212, doi:10.1006/jctb.2001.2047.
- Seymour, P. D. (1979), "On multicolourings of cubic graphs, and conjectures of Fulkerson and Tutte", Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society, Third Series 38 (3): 423–460, doi:10.1112/plms/s3-38.3.423, MR532981.
- Schwenk, Allen J. (1989), "Enumeration of Hamiltonian cycles in certain generalized Petersen graphs", Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B 47 (1): 53–59, doi:10.1016/0095-8956(89)90064-6, MR1007713.
- Shannon, Claude E. (1949), "A theorem on coloring the lines of a network", J. Math. Physics 28: 148–151, MR0030203.
- Skiena, Steven S. (2008), "Graph Problems Hard Problems", The Algorithm Design Manual (2nd ed.), Springer-Verlag, pp. 548–550, doi:10.1007/978-1-84800-070-4_16, ISBN 9781848000698. See also web site for this section of the book in the Stony Brook Algorithm Repository.
- Soifer, Alexander (2008), The Mathematical Coloring Book, Springer-Verlag, ISBN 9780387746401.
- Tait, P. G. (1880), "Remarks on the colourings of maps", Proc. R. Soc. Edinburgh 10: 729.
- Trahtman, Avraham N. (2009), "The road coloring problem", Israel Journal of Mathematics 172 (1): 51–60, arXiv:0709.0099, doi:10.1007/s11856-009-0062-5.
- Vizing, V. G. (1964), "On an estimate of the chromatic class of a p-graph", Diskret. Analiz. 3: 25–30, MR0180505.
- Vizing, V. G. (1965), "Critical graphs with given chromatic class", Metody Diskret. Analiz. 5: 9–17. (In Russian.)
- Williamson, D. P.; Hall, L. A.; Hoogeveen, J. A.; Hurkens, C. A. J.; Lenstra, J. K.; Sevast'janov, S. V.; Shmoys, D. B. (1997), "Short shop schedules", Operations Research 45 (2): 288–294, doi:10.1287/opre.45.2.288, JSTOR 171745, MR1644998.
- Zhou, Xiao; Nakano, Shin-ichi; Nishizeki, Takao (1996), "Edge-coloring partial k-trees", Journal of Algorithms 21 (3): 598–617, doi:10.1006/jagm.1996.0061, MR1417666.